How to Use GIT and GitHub PR via CLI
Nov. 09, 2022 · 8 min read
The world of software development is fascinating. Developing a product consist of three main choices, which are cheap, fast, and quality. Choosing your best categories can help your team in the future. Software development is composed of different tools that you can use to make your work more efficient and correct, choosing whether you go fast or right. How about both fast and right at the same time? Is that the best thing to do?
In this article, I will discuss what is Git? and what is version control? and its importance in software development as a programmer must learn or have in their “arsenal” of skill sets.
What is Git?
As for now, Git holds the record as by far the widely known and use version control system today. Git is an open-source project developed by Linus Torvalds (2005), also known as the lead developer in creating the Linux kernel. Almost all projects, both commercial and open-source rely on Git. Git was widely used by developers across the map because it supports various operating systems and IDEs.
Version Control and its importance
Version control, also called source control, is the practice of tracking and managing changes from the code project. The goal of a source control system is to help developers to track and manage changes to the project source code for a faster and smarter way of sharing your codes. How does the version control system track? every modification that happened on the project is being tracked in a git database. If developers do mistakes, they can easily be fixed by turning back to the earlier version when the project code was working fine.
How to get started with Git? If you are planning to use Git, here is the first thing you need to do. Install Git using the terminal.
Follow these steps:
- Open your terminal
-
Use and paste this command in your terminal -
brew install git. - Click enter and wait for the installation to complete
If you can install Git on your local machine successfully. Next is to install the Git credential manager.
What is Git Credential Manager?
Git Credential Manager also called GCM, it is another way of storing your credentials in remote hosting software for managing Git remote repositories. With GCM you don’t have to manually create your access credentials/token, in which GCM will automatically authenticate your credentials on your behalf.
To install the Git credential manager.
Follow these steps:
- In the same terminal after you install git
-
Use and paste this command in your terminal -
brew install git-credential-manager. - Click enter and wait for the installation to complete.
How to use Git?
Here’s how just follow the steps on how can you use Git to clone on a remote repository (Github).
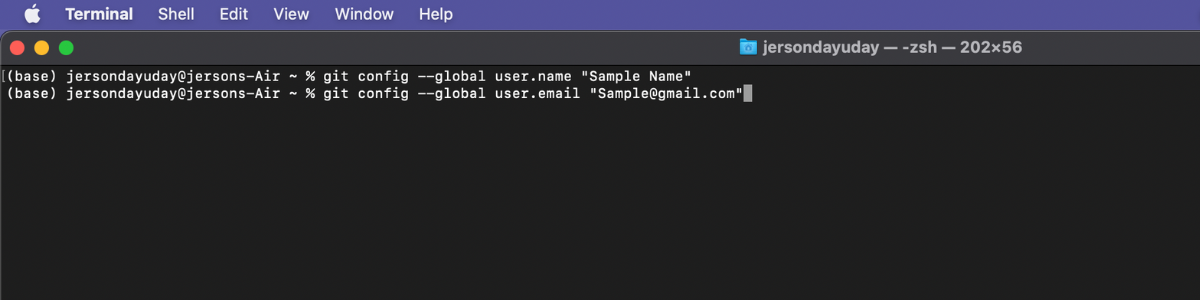
Step 1: Using terminal configure your git credentials using this two commands
git config --global user.name [your name on Github]press enter.git config --global user.email [your username or email used in Github]press enter.
Sample:
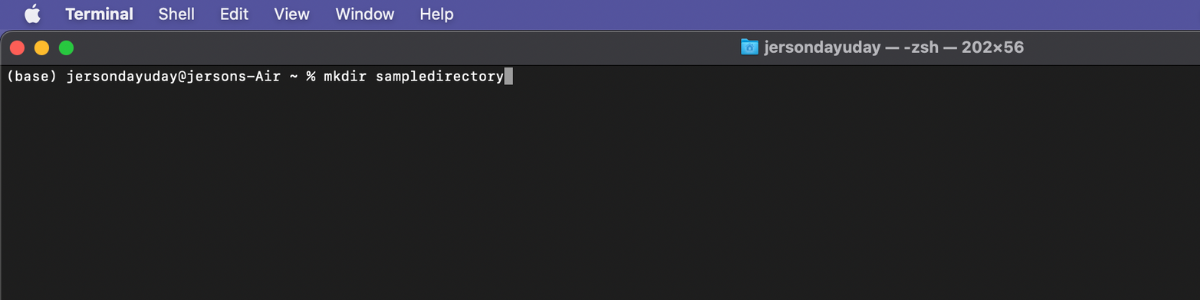
Step 2: After you able to configure your credential in git, make a new directory that you can work on for the repository.
Use this command mkdir [folder name] to create your working directory.
Step 3: To check if created your folder use this command ls and check if you created your folder.
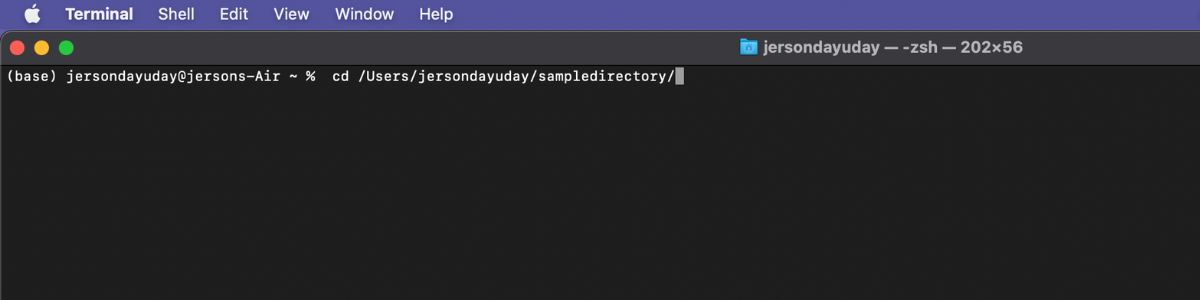
Step 4: Time to clone git repository from remote server (GitHub). In order to clone, first you need to change directory using cd [path folder].
Sample:
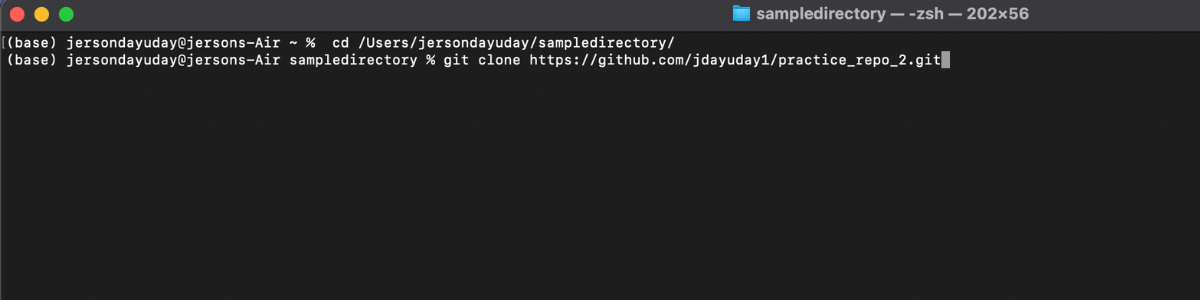
Step 5: Use git clone command git clone [https / ssh] and enter. Wait for the cloning process to finish.
Sample:
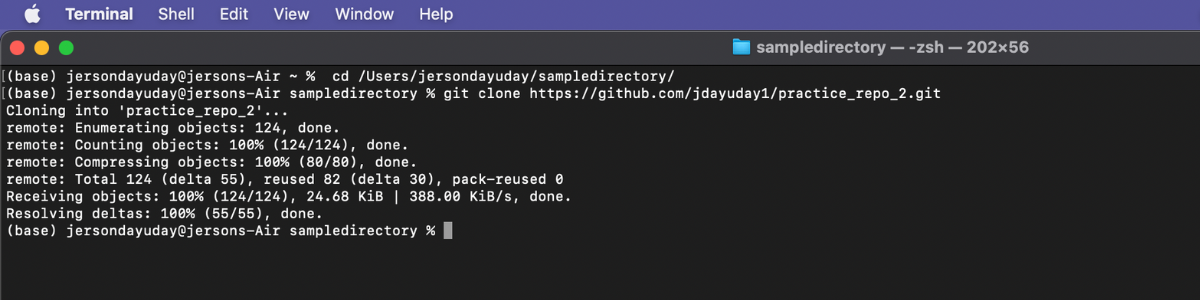
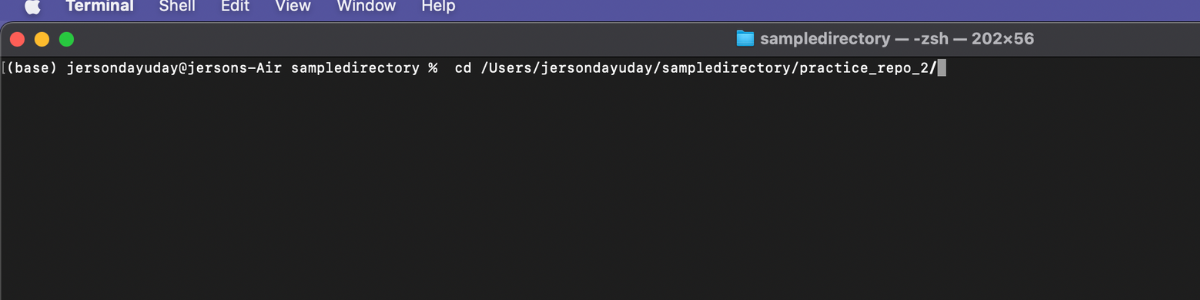
Step 6: After cloning the repository you need to change your directory to the exact folder of repository.
Sample:
Step 7: Check the status of your cloned repository using this command git status and enter.
Sample:
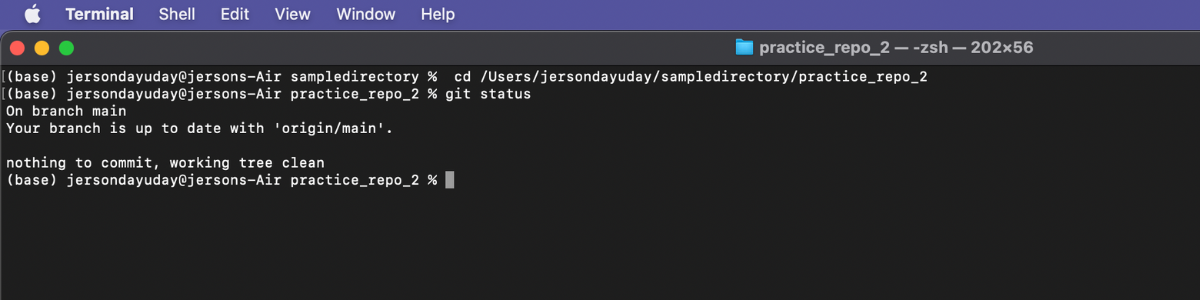
This is one of the ways in cloning a remote repository in GitHub.
Additional basic git commands that you can use are the following:
- git add -
git add .add / stages changes you made. - git commit -
git commit -m"Your commit message"captures a snapshot of the project’s currently staged changes. - git push -
git push origin [branch name]upload local repository content to a remote repository. - git help -
git --helpshow alla available command for git.
Git Do’s and Don’t important to remember!
These are the following **Git Do’s:**
- Create a Git repository for every new project.
- Always create a new branch.
- Always commit changes with a concise and useful commit message.
- Keep your branch up to date with development branches.
- Always create a pull request for merging changes from one branch to another.
- Always review your code once by yourself before creating a pull request.
- Include read/write permission access control to repositories to prevent unauthorized access.
- Add protection for special branches like master and development to safeguard against accidental deletion.
These are the following **Git Don’t:**
- Don’t commit directly to the master or development branches.
- Don’t hold up work by not committing local branch changes to remote branches.
- Don’t create one pull request addressing multiple issues.
- Don’t work on multiple issues in the same branch. If a feature is dropped, it will be difficult to revert changes.
- Don’t reset a branch without committing/stashing your changes. If you do so, your changes will be lost.
- Don’t do a force push until you’re extremely comfortable performing this action.
These things are important to remember and practice especially if you are working on a public/company repository. In following this Do’s and Don’t list you may be able to work efficiently and avoid the disruption of workflow.
How to creat a pull request using GitHub CLI
What is GitHub CLI? GitHub CLI Pull requests, problems, GitHub Actions, and other GitHub features are brought to your terminal, allowing you to conduct all of your work in one spot.
Steps to follow in creating a pull request using GitHub CLI.
Step 1: Install GitHub CLI using this command and past it on your terminal - brew install gh.
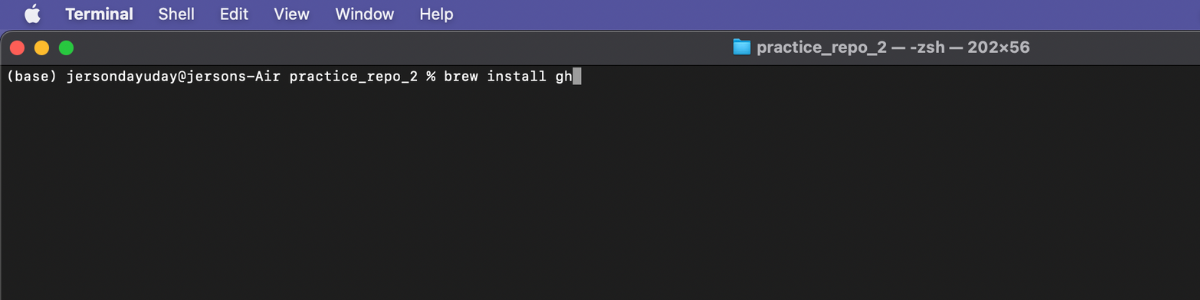
Step 2: After installing GitHub CLI, You go to your working directory.
Step 3: In your working directory use this command gh auth login and enter.
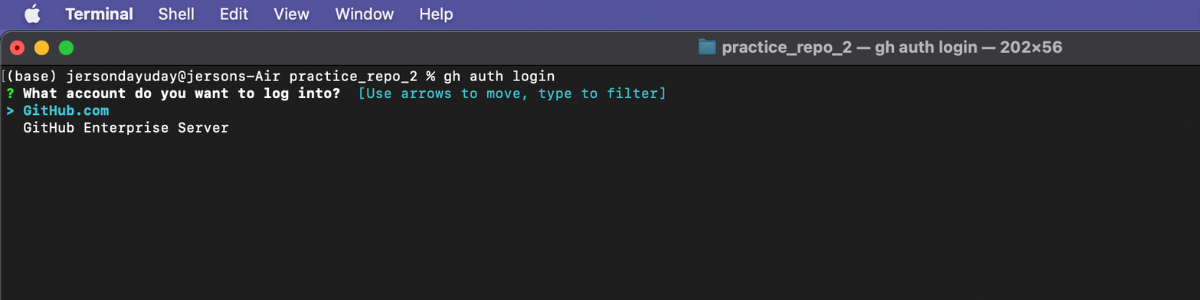
Just follow the given instructions for GitHub login credentials.
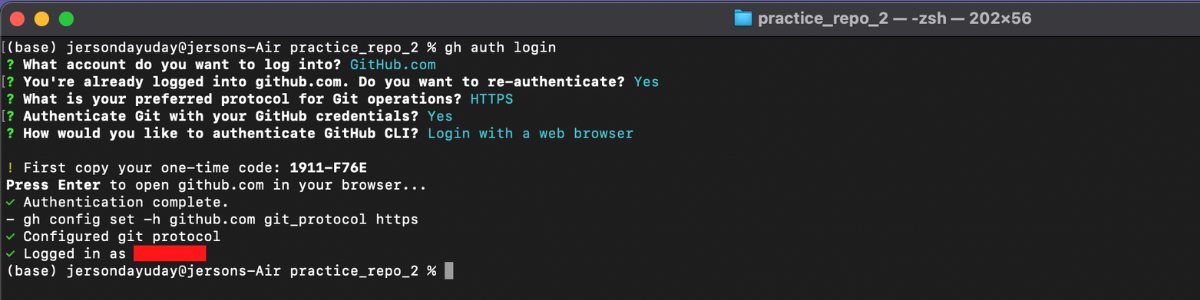
Step 4: It is a good practice to create another branch that you can work on, instead of working directly to the main/origin branch. This command will help to create a branch git checkout -b [branchname]
Sample:
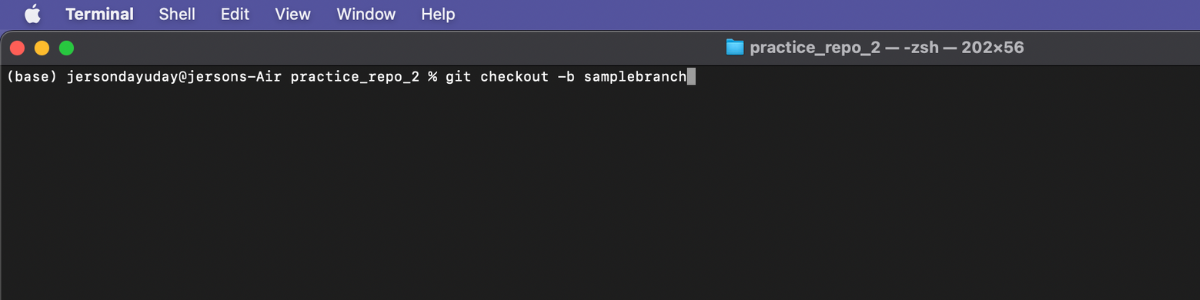
Step 5: In requesting a Pull Request in GitHub CLI. Let’s assume that you already make some changes on your working directory/branch and you already commit and push your changes. Now let’s make a pull request out of it, using GitHub CLI.
There are a different way of a request for a pull request in GitHub CLI, this is one of the sample commands that you can use gh pr create --title [Put your title here] --body [put the body of the pull request you are requesting] [PR link].
Sample:
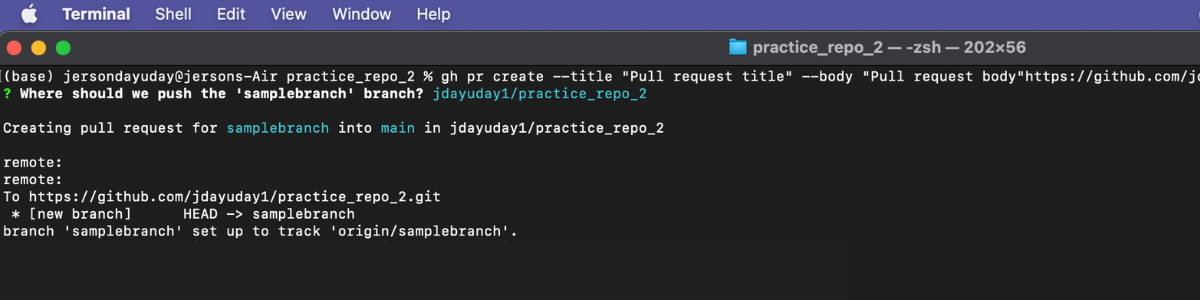
Additional tip!
In using Git and GitHub credentials it’s a best practice to use your private email, rather than using your public GitHub in authenticating credential in CLI. To find your private email, follow the following steps:
Step 1: Navigate to your GitHub, in the top-right corner of your GitHub homepage you find your profile icon.
Sample:
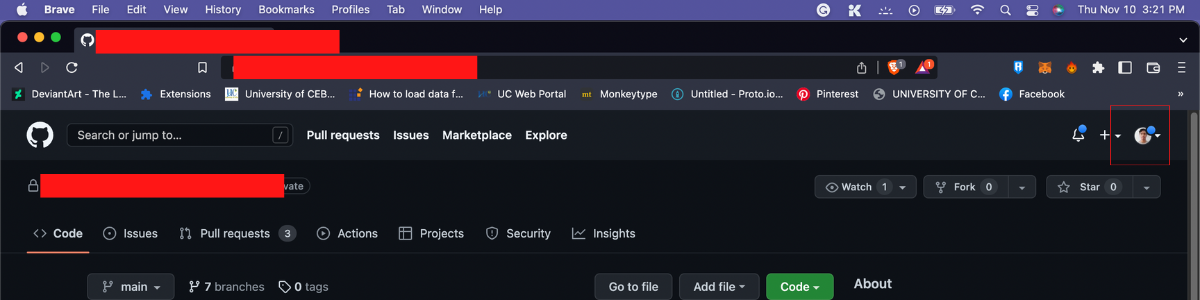
Step 2: Navigate to the dropdown menu and select “setting”.
Sample:
Step 3: Inside the setting, select email.
Sample:
Step 4: In your email setting, navigate below, and you will find the primary email address section, you can see your private email for your GitHub account.
Sample:
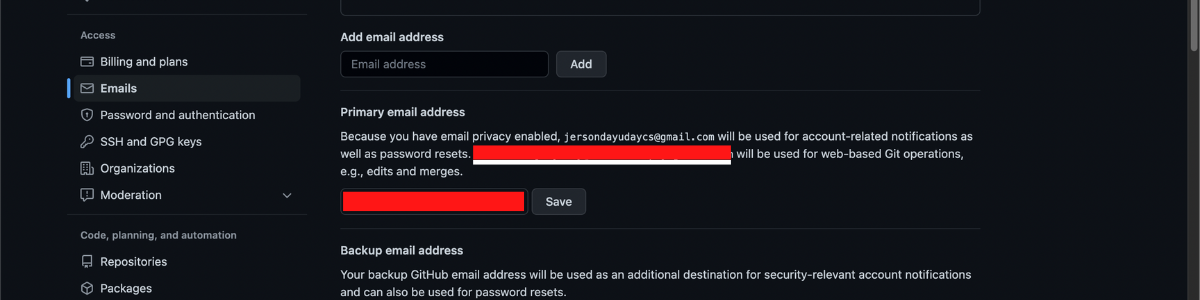
Remember! for best practices in using Git and GitHub always use your private emails. To know more about Git and GitHub pull request process you can check this article What is a Pull Request, the Process, and Why (Sagnoy, 2022)
Conclusion
Git is an open-source project developed by Linus Torvalds (2005), also known as the lead developer in creating the Linux kernel. Git was widely used by developers across the map because it supports various operating systems and IDEs.
The goal of a source control system is to help developers manage changes to the project source code. If you are planning to use Git, here is the first thing you need to do. Every modification that happened on the project is being tracked in a git database. These are the Git Dos and Git Don’ts for developing a strong and maintainable codebase.